OPTICAL FIBRE
An optical fibre is a thin strand of glass or plastic that serves as a transmission medium over which the information passes. To be more technical, an optical fibre
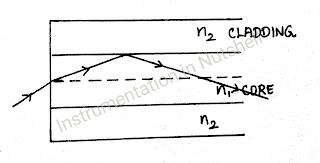
is a dielectric waveguide that operates at optical frequencies (1013 to 1016 Hz) and transfers information in the form of light by the mechanism of total internal reflection. The optical fibre consist of a central core surrounded by a cladding layer.
Types of Optical Fibres
The different types of optical fibres are,
An optical fibre is a thin strand of glass or plastic that serves as a transmission medium over which the information passes. To be more technical, an optical fibre
is a dielectric waveguide that operates at optical frequencies (1013 to 1016 Hz) and transfers information in the form of light by the mechanism of total internal reflection. The optical fibre consist of a central core surrounded by a cladding layer.
Types of Optical Fibres
The different types of optical fibres are,
- Step index and Graded index fibre based on refractive index profile
- Single mode and multimode fibre based on number of modes
- Glass, Plastic clad and All plastic fibres based on material
Comparison
A detailed comparison of different types of optical fibres is presented below:
1. Step Index and Graded Index Fibre
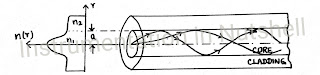
This classification is based on the refractive index profile of core and cladding. Refractive index or Index of Refraction is the fundamental optical parameter of a medium. The value of refractive index shows how a ray of light travels in a medium.
A detailed comparison of different types of optical fibres is presented below:
1. Step Index and Graded Index Fibre
This classification is based on the refractive index profile of core and cladding. Refractive index or Index of Refraction is the fundamental optical parameter of a medium. The value of refractive index shows how a ray of light travels in a medium.
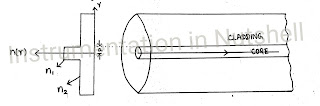
Step index fibre
|
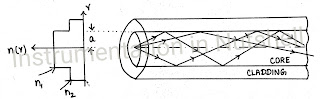
Graded index fibre
|
It is a fibre in which the refractive index of the core is uniform
throughout the length of the fibre .
|
The refractive index of the core is not constant.
|
|
|
|
The ri of the cladding is slightly less than that of the core
|
The ri is maximum at the axis of the core and it decreases from core
to cladding.
|
The diameter of the core is about 50 to 200µm in the case of multimode
fibre and 10µm in case of single mode fibre
|
The diameter of the core is about 50µm in the case of multimode
fibre
|
The losses and pulse distortion are high
|
The losses and pulse distortion are reduced because of the self-focusing
effect.
|
Information carrying capacity is less
|
The information carrying capacity is increased.
|
2. Single Mode and Multi Mode Fibres
Mode describes the path of propagation of light ray along the optical fibre. The pattern of light ray propagation classifies fibres into single mode and multi mode.
Mode describes the path of propagation of light ray along the optical fibre. The pattern of light ray propagation classifies fibres into single mode and multi mode.
Single mode fibres
|
Multi mode fibres
|
||
| |||
The core diameter is narrow (2 to 10µm)
|
The core diameter is wide (>50µm)
|
||
The refractive index difference between core and cladding is very
small.
|
The refractive index difference between core and cladding is large.
|
||
The single mode fibers are always step index as the core is narrow
which cannot be made graded index.
|
It can be made by either step index or graded index fibre, since the
core is wide.
|
||
Only LASER can be used as the optical source.
|
LED and LASER are used as optical source.
|
||
There is no dispersion because of no degradation of signals during
its propagation through the fibre.
|
There is signal distortion due to multimode dispersion and material
dispersion.
|
||
These are suitable for long distance communication because of its
greater information carrying capacity.
|
Large dispersion and attenuation limits its application to short
distance communication. These fibres are used in Local Area Network.
|
||
Launching of light into these fibres and joining two fibres are very
difficult.
|
Launching of light into these fibres and joining two fibres are easy.
|
||
Fabrication is very difficult making it costlier.
|
Fabrication is comparatively easier and it is not costly.
|
3. Glass,Plastic Clad and All Plastic Fibres
An optical fibre is usually made of glass. It can also be made out of plastic inorder to add strength to it. Based on the material of fabrication of optical fibre, it is categorised into Glass, Plastic clad and All plastic fibres.
An optical fibre is usually made of glass. It can also be made out of plastic inorder to add strength to it. Based on the material of fabrication of optical fibre, it is categorised into Glass, Plastic clad and All plastic fibres.
Glass fibres
|
Plastic
clad fibres
|
All plastic fibres
|
In glass fibres, both the core and cladding are made of glass
consisting of either silica or a silicate.
|
Plastic clad fibres have a plastic cladding made of silicone rubber
and a glass core made of silica.
|
All plastic fibres have plastic core and cladding.
|
Glass fibres resist deformation at temperatures as high as 1000˚C, thermal shock and are highly transparent.
|
These fibres exhibit lower radiation induced losses and have an
improved performance.
|
The plastic core and cladding reduces the requirement of buffer
jacket for fibre protection.
|
Losses are less.
|
Medium losses
|
High losses
|
Mechanical strength is poor.
|
Mechanical strength is medium
|
Large mechanical strength.
|
These are used for long distance communication because of low losses.
|
These are used for medium distance communication.
|
These fibres are used for very short-haul low cost links.
|












No comments:
Post a Comment
Share your reading experience here