Ratio control systems are special form of feedforward control systems where two variables are measured and maintained at a constant
ratio in order to control a third variable. Ratio control is applied to keep up
certain ratio between two or more flow rates in process industries.
The stream whose flow rate can be measured but cannot
be controlled is referred to as wild stream or master stream. The other flow
which can be measured and controlled is called as controlled flow or stream.
The ratio controller manipulates the controlled flow to maintain the desired
ratio between the two flows.
If it is assumed that A and B are to be two flows, then
the desired ratio is given by,
R
= B/A …..(1)
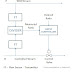
Ratio control configuration 1
 |
Ratio control configuration 1
|
The flow rates A(wild flow) and B(controlled flow) are
measured and their actual ratio is calculated. The actual ratio is compared
with the desired ratio to find the deviation between them. The ratio controller
regulates the controlled flow appropriately.
The advantage of this configuration is that the actual
ratio is measured.
The key disadvantage is that this configuration
includes the divider in the closed loop. The process gain varies inversely with
the flow B which results in highly nonlinear control loop and instability.
To find the loop gain, differentiate the equation (1)
with respect to flow B
It’s clear that the loop gain varies inversely with flow B.
The ratio can be inverted and is given by, R = A/B …..(3)
Differentiating the equation (3) gives the loop gain,
The result is same in the case of inverted ratio.
We shall check for flow-squared signals. For this case, ratio is
Differentiating the equation (5) gives the loop gain,
Once again, the loop gain varies inversely with flow B.
It makes this configuration invalid for practical
applications.
Ratio control configuration 2
 |
Ratio control configuration 2
|
This is the configuration that is practically used in
control applications.
Applications of Ratio Control
Maintain the ratio of two reactants entering a reactor
Keep a specified reflux ratio in a distillation column
Set the ratio of component streams constant in blending
operations
Keep the ratio of fuel and air at its optimum value for
the most efficient combustion in a furnace
Hold the ratio of feed flow rate and steam a constant
in the reboiler of a distillation column
Example of Ratio Control
Neutralisation of Wastewater
The wastewater will be acidic in nature. In the process of neutralisation, the base (Sodium Hydroxide, NaOH) is added to bring up the pH level and neutralise the liquid. Here, the flow rate of wastewater and the flow rate of NaOH solution are to be maintained at a ratio. The ratio is determined by the pH controller based on the pH value of the effluent. The product of pH controller output and measured flow rate of wastewater acts as a setpoint for NaOH solution flow controller. The flow controller actuates the control value based on setpoint and measured flow rate of NaOH solution. Thus, the addition of NaOH is controlled and the ratio of two flow rates are maintained.
Also read other control schemes
Example of Ratio Control
Neutralisation of Wastewater
 |
Ratio Control in Neutralisation of Wastewater
|
Also read other control schemes













No comments:
Post a Comment
Share your reading experience here